3.2 DMA control register
■ Level 2-0 DMA set register
● Read address
Figure 3.1 Level 2-0 read address (registers: D0R, D1R, D2R) Initial value is undefined
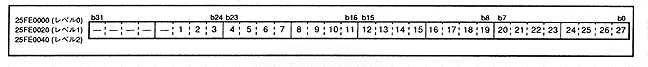
DxR26-0 [x = 2-0] (R / W) DMA level 2-0 Read address bit26-0
Export address
Figure 3.2 Level 2-0 write address (Register: D0W, D1W, D2W) Initial value is undefined

DxW26-0 [x = 2-0] (R / W) DMA level 2-0 Write address bit26-0