Return to previous page | Return to menu | Go to next page
Normal scroll screen scaling
Among the normal scroll screens, “NBG0, NBG1” can be scaled (maximum: 1/4 to 256 times). An image of this is shown below.
Figure 8-20 Image of scroll enlargement / reduction
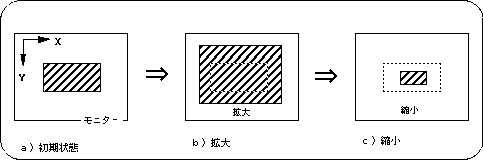
The scope of scrolling using the normal scroll screen “NBG0, NBG1” varies depending on the reduction setting of the scroll function setting.
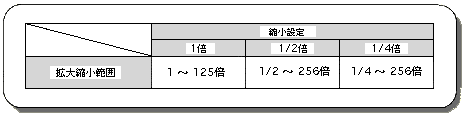
Table 8-20 Change of enlargement / reduction range by reduction setting
Use the library function “slZoomNbg0,1” corresponding to the normal scroll screen “NBG0, NBG1” respectively to enlarge / reduce the normal scroll screen in SGL.
- [void slZoomNbg0,1 (FIXED scale_x, FIXED scale_y);]
- Enlarge / reduce the normal scroll screen “NBG0, NBG1”.
For the parameter, substitute the reciprocal of the horizontal and vertical magnification.
For example, if you want to enlarge to 2 times, assign 1/2 to the parameter, and if you want to reduce it to 1/2, assign 2.
The limit value that can be selected for the reduction range varies depending on the reduction setting (see the table above).
About parameter setting for scaling function
It is necessary to substitute the reciprocal of the desired multiple for the parameter used for scaling the scroll (for example, 1/2 if you want 2.0 times).
This is because the value indicated by the parameter does not directly represent the scale value.
The value assigned as the parameter of the enlargement / reduction function indicates the amount of movement to the next dot to be displayed after scrolling 1 dot.
If you specify 2.0 as the amount of movement, the scroll will skip one dot at a time and the next dot will be displayed. As a result, the scroll will be reduced by a factor of 1/2.
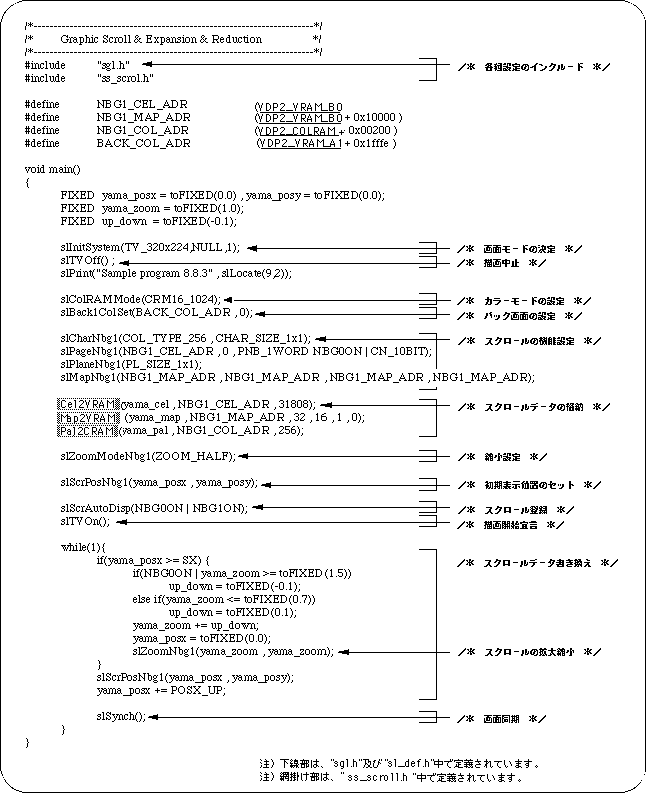
The following sample program (Listing 8-4) is an example of actually scaling the normal scroll screen using the SGL library function.
List 8-4 sample_8_8_3: Scroll scaling
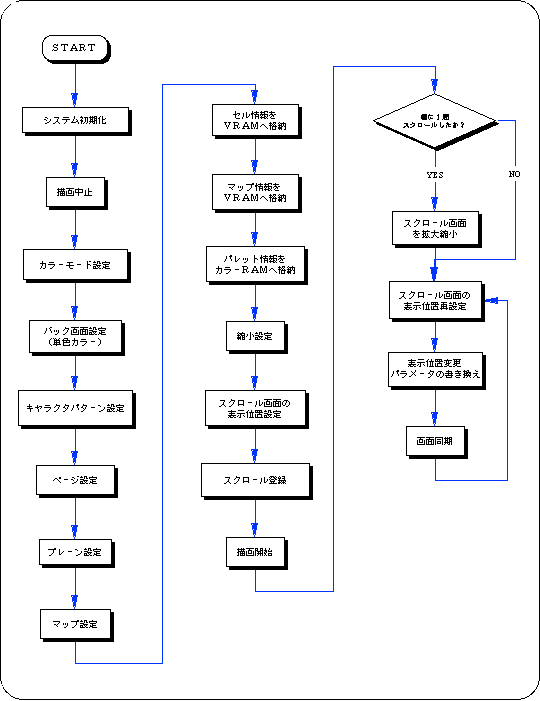
Flow 8-5 sample_8_8_3: Scroll enlargement / reduction
Return to previous page | Return to menu | Go to next page



