Return to previous page | Return to menu | Go to next page
Clipping is the process of removing the part that protrudes from the display area (the area that is actually projected onto the projection plane) and hiding it. SGL can use this concept to set a window for the projection plane. Therefore, we will first explain the concept of clipping, and then explain the actual window setting on SGL.
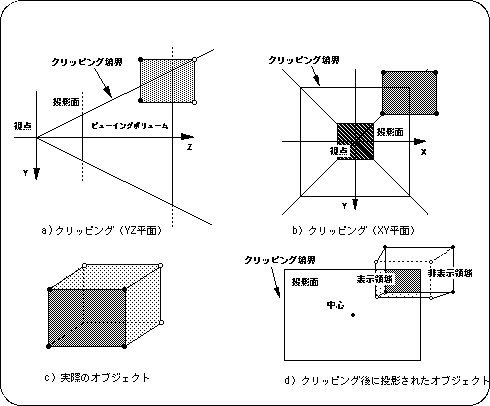
First, let's illustrate the concept of clipping with a 2D graphics example. In the case of 2D graphics, display / non-display is switched between inside and outside the separated rectangular area.
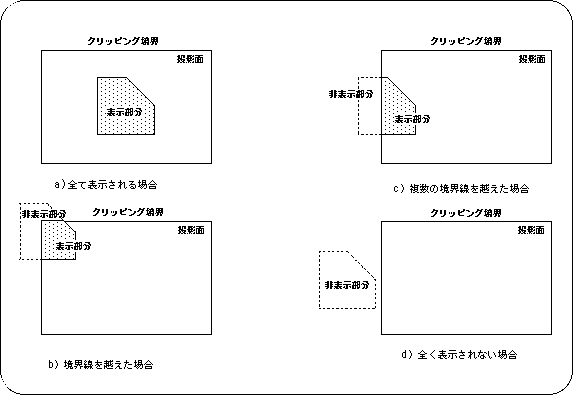
The example below shows a display example when an object to be displayed is placed inside or outside the display area given as a rectangular area.
Note) When the projection plane closed by the clipping boundary is used as the display area
As shown in the figure above, the object that is the target of clipping can be displayed or hidden within and outside the clipping area. In this example, when one object covers both of the clipping areas, part of the object (inside the area) is displayed and part (outside the area) is not displayed.
Caution
In some cases, display / non-display may be switched depending on the ratio of one object included in the clipping area due to problems with calculation speed and drawing speed.
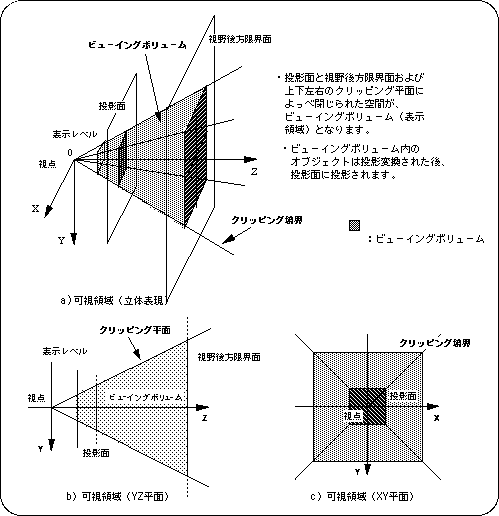
In 3D graphics, the visual field pyramid is usually determined by the perspective transformation matrix, and the inside of this pyramid is defined as the display area and the outside of the pyramid is defined as the non-display area. Objects in the display area are projected onto the projection surface and projected on the monitor.
This viewing pyramid is clipped by a closed space (viewing volume) surrounded by the following six planes.
Left side of field: Clipping plane (determined by angle of view) Right side of field of view: Clipping plane (determined by angle of view) Top of view: Clipping plane (determined by angle of view and screen mode) Bottom of view: Clipping plane (determined by angle of view and screen mode) Front of view: front limit plane (determined by function “slZdspLevel”) Rear face of field of view: Rear limit surface (determined by parameter “Zlimit” in function “slWindow”)
In the case of SGL, in addition to this, it is possible to add additional clip planes (refer to “4.5: Window” for details).